Hip pain and discomfort can significantly impact daily activities, but not all hip problems require surgical intervention. Conservative management focuses on non-surgical treatments aimed at reducing pain, improving function, and enhancing the quality of life. These approaches are often effective for a wide range of hip conditions, including osteoarthritis, bursitis, tendinitis, and early stages of hip labral tears.
Lifestyle Modifications
• Weight Management: Excess body weight can increase stress on the hip joints. Losing weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help alleviate pain and improve joint function.
• Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that exacerbate hip pain, such as high-impact exercises, can prevent further damage. Switching to low-impact activities like swimming or cycling can help maintain fitness without straining the hip.

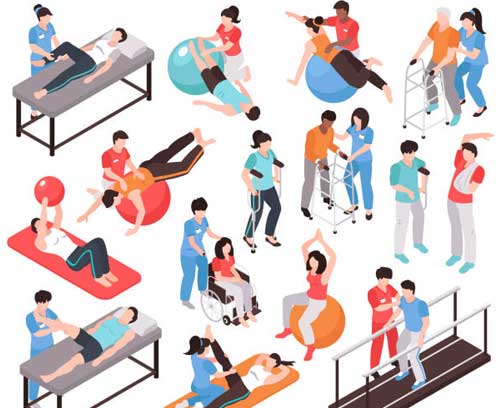
Physical Therapy
Exercise Programs: A tailored exercise program designed by a physical therapist can strengthen the muscles around the hip, improve flexibility, and reduce pain. Key exercises include stretching, strengthening, and range-of-motion activities.
Manual Therapy: Techniques such as joint mobilization, massage, and manipulation can reduce stiffness and improve joint function.
Gait Training: For patients with altered walking patterns due to hip pain, gait training can help restore normal walking mechanics and reduce the load on the hip.

Medications
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
Pain Relievers: Acetaminophen can be used to manage pain, especially for those who cannot tolerate NSAIDs.
Topical Treatments: Creams or gels containing NSAIDs or capsaicin can be applied directly to the hip area to provide localized pain relief.
Injections
Corticosteroid Injections: These injections can provide significant relief from inflammation and pain in conditions like bursitis or arthritis. The effects are typically temporary but can help manage acute flare-ups.
Hyaluronic Acid Injections: Although less common, these injections can help lubricate the hip joint in osteoarthritis, reducing pain and improving mobility.
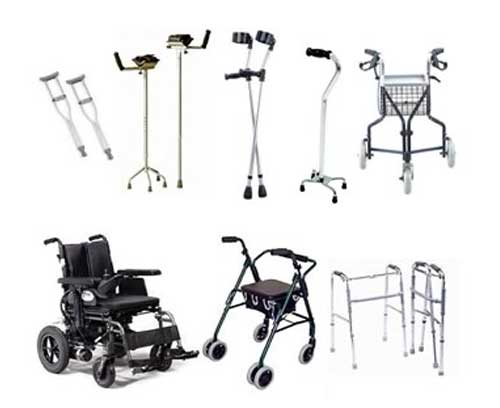
Assistive Devices
Canes or Walkers: Using a cane or walker can offload the hip joint, reduce pain during walking, and prevent falls.
Orthotics: Shoe inserts or custom orthotics can improve alignment and reduce stress on the hip joint.

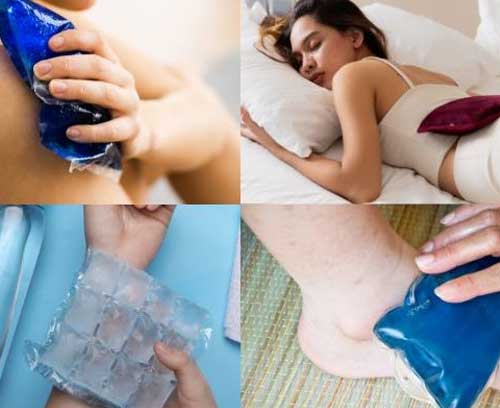
Heat and Cold Therapy
Cold Therapy: Applying ice packs to the hip can help reduce inflammation and numb acute pain.
Heat Therapy: Heat pads or warm baths can relax muscles, improve circulation, and alleviate chronic pain and stiffness.

When to Consider Conservative Management
Conservative management is often the first line of treatment for many hip conditions, particularly when symptoms are mild to moderate. It is suitable for individuals who prefer to avoid surgery or those for whom surgery poses significant risks due to age or other health conditions.
Why Choose Dr. Chintan Patel for Conservative Hip Management
Dr. Chintan Patel offers comprehensive conservative management options tailored to each patient’s specific needs and lifestyle. With a focus on personalized care, Dr. Patel works closely with patients to develop effective non-surgical treatment plans that aim to reduce pain, restore function, and improve overall quality of life.
